 Image:
Image:
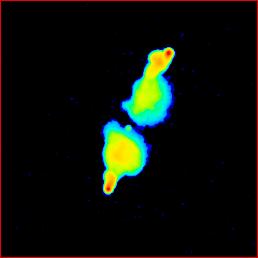
The radio core is the compact feature on the north edge of the
souther lobe, close to the line connecting the hotspots.
The hotspots project some distance out from the relatively relaxed bridge,
giving the lobes a bottleneck structure. Similar structures are quite common
in classical doubles (there are at least five cases in this Atlas), but
3C 184.1 is a particularly clear example. The structure suggests that
the hotspots have suddenly become able to push outwards faster than
before, perhaps because of a drop in the density of the surrounding gas
at a certain radius, for instance at the boundary between
the host galaxy's atmosphere and the start of the true
inter-galactic medium.
The same effect could arise from a sudden increase
in the beam density and hence energy output,
or from a stabilization of a jet that had previously
wobbled around in its pointing direction.
Higher-resolution images of the hotspots are given by
Leahy et al. (1997), who note a possible
jet feeding in to the north hotspot.
Page created: 2009 Apr 2 14:16:42
J. P. Leahy
jpl@jb.man.ac.uk
 Image:
Image: