Wonder - A Scientific Oratorio
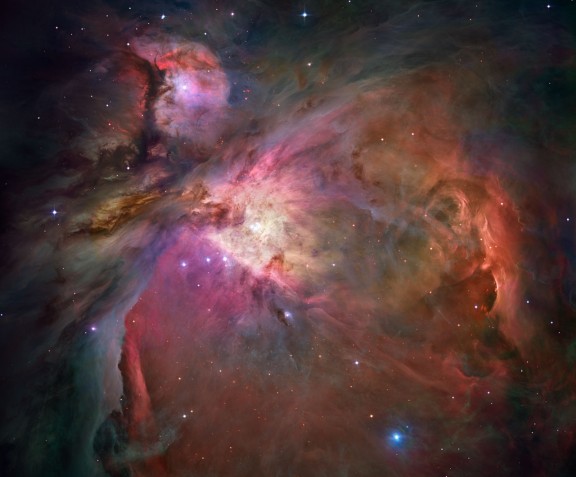

The Orion Nebula - a nearby cloud of gas and dust where stars are being born.
Credit: NASA, ESA, M. Robberto (STScI/ESA) and
The Hubble Space Telescope Orion Treasury Project Team .
Theme 4 - The birth of stars
In the first few hundred million years after the Big Bang, gravity caused giant clouds of gas to collapse. Eventually nuclear fusion began at the heart of these collapsing clouds and the first stars began to shine.
The first structures to form in the Universe were clumps of dark matter collapsing in on themselves due to their own gravity. "Normal" gas made up of the elements created during the Big Bang (mostly hydrogen and helium) eventually collapses in on these dark matter seeds attracted by their gravity.
These collapsing clouds of gas become very dense and hot at their cores. Conditions are so extreme here that protons (the nuclei of hydrogen atoms) can crash together to make helium nuclei in nuclear fusion reactions. This provides a huge amount of energy, enough to make the dense cloud of gas begin to shine brightly and the first stars were born. This was the end of the Dark Ages, a few hundred million years after the Big Bang.
Following this, galaxies form as many clumps of dark matter, stars and gas merge together. Then giant clusters of galaxies form.