Monthly Night Sky Guide July 2023
Compiled by Ian Morison
This page, updated monthly, will let you know some of the things that you can look out for in the night sky. It lists the phases of the Moon, where you will see the naked-eye planets and describes some of the prominent constellations in the night sky during the month.
New(ish)
The author's: Astronomy Digest
which, over time, will provide useful and, I hope, interesting articles for all amateur astronomers. A further aim is to update and add new material to link with the books recently published by Cambridge University Press and which are described on the home page of the digest. It now includes well over 100 illustrated articles.Image of the Month

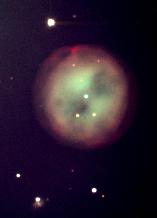
Planetary Nebula, M27, in Vulpecula
Messier 27, sometimes called the Apple Core Nebula, is the brighest Planetary Nebula in the northern sky and high in the southern sky this month. Having a magnitude of 7.5, it can just be picked out in binoculars under a dark, moonless, sky. It lies at a distance of about 1,360 light years and has an angular diameter of 8 arc minutes. From its rate of expansion, its age has been estimated to be about 10,000 years. Planetary Nebula are the remnants of stars like our Sun whose outer parts have been throw out into space leaving the core which has reduced in size to about the size of the Earth - called a White Dwarf - whose temperature may well exceed 100,000 Kelvin. It is seen as a faint star at the centre of the nebula.
The image was taken by the author using a 9.25 inch Celestron Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope and processed using the 'Photometric Colour Calibration' tool in the astrophotography imaging program, Siril. (See articles in the Astronomy Digest.) This compares the star colours in the captured image with those in the NOMAD or APASS star catalogues to give a very accurate colour balance. The heart of the nebula has thus appeared a 'teal' colour accurately giving the combined colour of the Oxygen III and Hydrogen Beta spectral lines.
Highlights of the Month
July - late night: Noctilucent Clouds
This month, if clear, there is still a chance of observing Noctlucent Clouds towards the North. They exist at heights of 76-85 km - higher than any other clouds in the Earth's atmosphere - and are composed of tiny crystals of water ice. Generally seen in the northern hemisphere from latitudes 45 to 80 degrees north. They often resemble thin, streaky, cirrus clouds and are usually blue or silver in colour. Look towards the NNW before midnight and NNE afterwards.
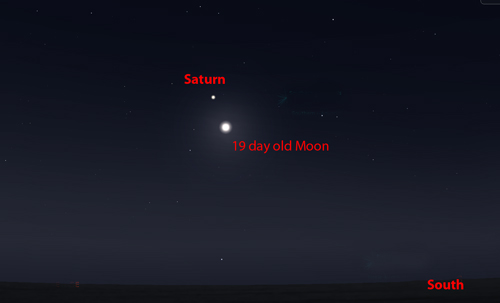
July 7th - before dawn: Saturn and the Moon.
Looking towards the east-southeast before dawn Saturn will be seen lying above the crescent Moon.
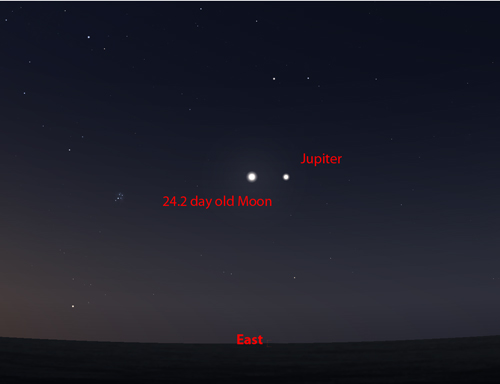
July 12th - before dawn: Jupiter and a waning crescent Moon.
This morning, if clear, and looking towards the east one could spot Jupiter just to the right of a waning crescent Moon.
July 21st - after sunset: Planets and a very thin waxing crescent Moon.
Just after sunset and given a very low horizon to the west, you may be able to spot Mars, Venus and Mercury below the crescent Moon.
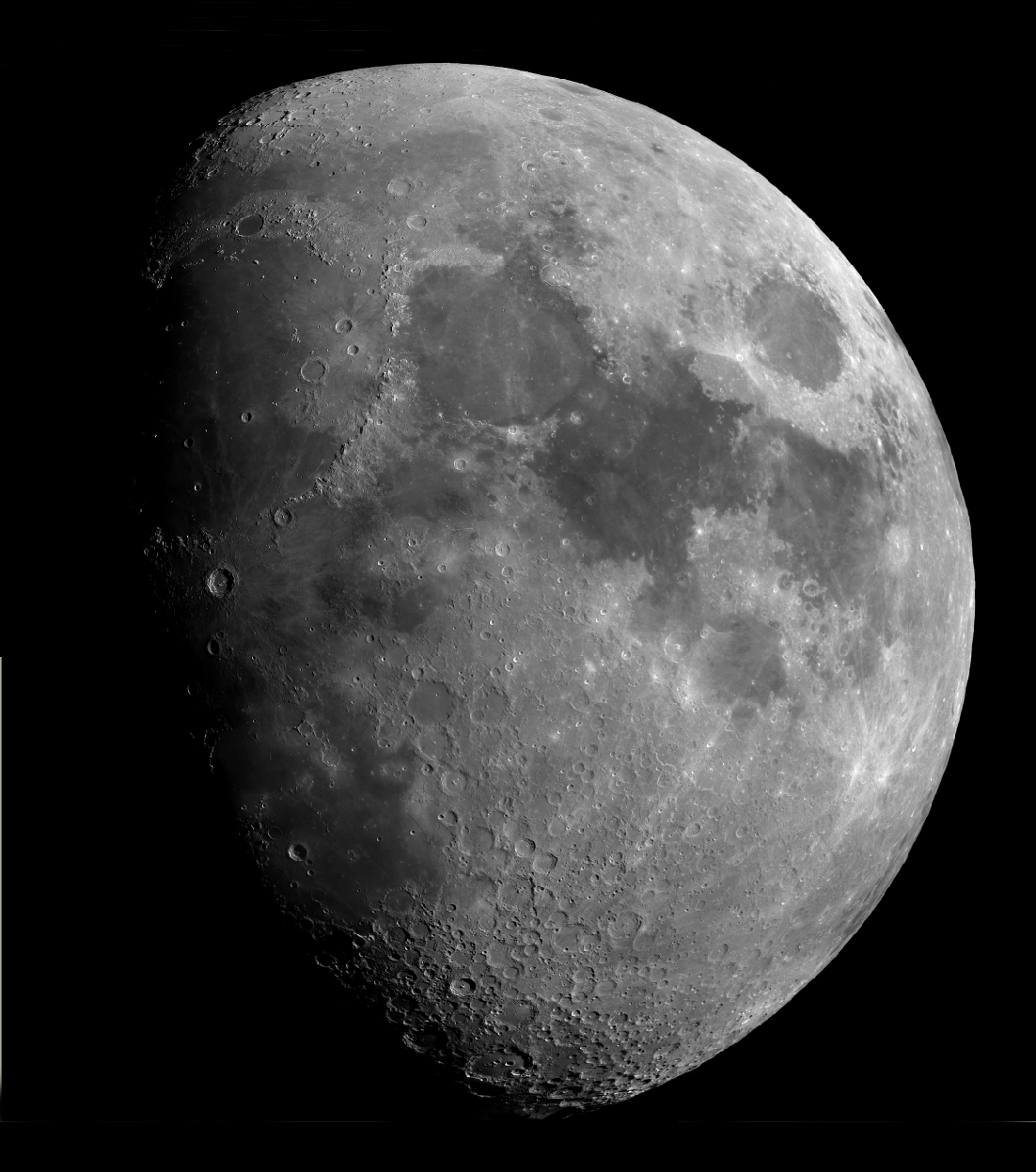
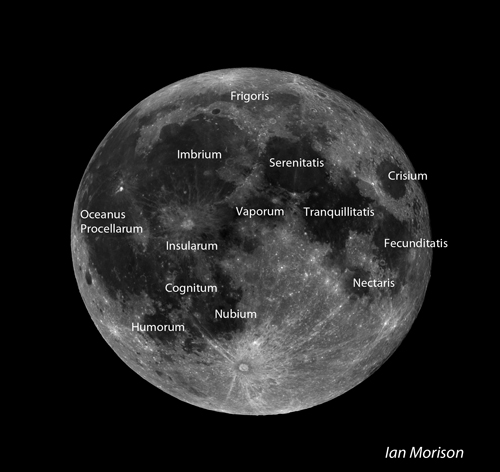
Learn the Mare on the Moon.
Why not use the annotated image of the full Moon to learn the locations of the Moon's Mare. You can see some of them with your unaided eye and binoculars will enable you to spot them all.
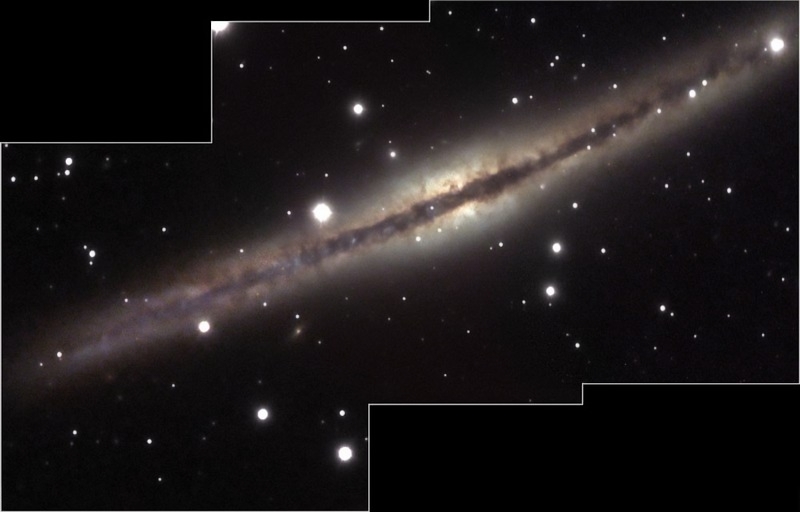
NGC 891 imaged with the Faulkes Telescope
Galaxy NGC 891, imaged by Daniel Duggan.
This image was taken using the Faulkes Telescope North by Daniel Duggan - for some time a member of the Faulkes telescope team. NGC 891 is an edge-on spiral lying in the constellation Andromeda at a distance of 27 million light years. We think that this is very much as our own galaxy might look when seen edge-on.
Learn more about the Faulkes Telescopes and how schools can use them: Faulkes Telescope"
The Moon

The Moon at 3rd Quarter. Image, by Ian Morison, taken with a 150mm Maksutov-Newtonian and Canon G7.
Just below the crator Plato seen near the top of the image is the mountain "Mons Piton". It casts a long shadow across the maria from which one can calculate its height - about 6800ft or 2250m.
| new moon | first quarter | full moon | third quarter |
|---|---|---|---|
| July 18th | July 26th | July 3rd | June 10th |
Some Lunar Images by Ian Morison, Jodrell Bank Observatory: Lunar Images
A World Record Lunar Image
To mark International Year of Astronomy, a team of British astronomers have made the largest lunar image in history and gained a place in the Guinness Book of Records! The whole image comprises 87.4 megapixels with a Moon diameter of 9,550 pixels. The resolution of ~0.4 arc seconds allows details as small as 1km across to be discerned! The superb quality of the image is shown by the detail below of Plato and the Alpine Valley. Craterlets are seen on the floor of Plato and the rille along the centre of the Alpine valley is clearly visible. The image quality is staggering! The team of Damian Peach, Pete lawrence, Dave Tyler, Bruce Kingsley, Nick Smith, Nick Howes, Trevor Little, David Mason, Mark and Lee Irvine with technical support from Ninian Boyle captured the video sequences from which 288 individual mozaic panes were produced. These were then stitched together to form the lunar image.
Please follow the link to the Lunar World Record website and it would be really great if you could donate to Sir Patrick Moore's chosen charity to either download a full resolution image or purchase a print.
The 8 day old Moon
This image was taken by the author on a night in March 2018 when the Moon was at an elevation of ~52 degrees and the seeing was excellent. This enabled the resolution of the image to be largely determined by the resolution of the 200 mm aperture telescope and the 3.75 micron pixel size of the Point Grey Chameleon 1.3 megapixel video camera. The use of a near infrared filter allowed imaging to take place before it was dark and also reduced the effects of atmospheric turbulence. The 'Drizzle' technique developed by the Hubble Space Telescope Institute (HSTI) was used to reduce the effective size of the camera's pixels to allow the image to be well sampled. Around 100 gigabytes of data, acquired over a 2 hour period, was processed to produce images of 54 overlapping areas of the Moon which were then combined to give the full lunar disk in the free 'stitching' program Microsoft ICE. A further HSTI development called 'deconvolution sharpening' was then applied to the image. The Moon's disk is ~6,900 pixels in height and has a resolution of 0.6 to 0.7 arc seconds. Interestingly, as seen in the inset image, the rille lying along the centre of the Alpine Valley is just discernable and this is only ~0.5 km wide! [Due to size limitations the large image is 2/3 full size.]
The Planets
Jupiter
Jupiter is now visible in the eastern pre-dawn sky rising at 2 am BST. At the start of the month it will have a magnitude of -2.21 and an angular diameter of 36.55 arc seconds. By month's end it will be best seen in the east around 4 am BST with an elevation of 19 degrees. It rises at midnight and its brightness will have then increased a touch to -2.8 and its angular size to 39.71 arc seconds.
Saturn
Saturn. Early this month Saturn may be spotted before dawn in the east-southeast having a magnitude of 0.8 having risen at midnight BST. Its angular size will then be 18 arc seconds with its rings spanning some 42 degrees. By month's end it rises at 22:30 BST will be best seen an hour before dawn further round to the south-southeast, then having a magnitude of 0.6 and an angular diameter of 18.73 arc seconds.
Mercury
Mercury may just be visible after sunset in the west on the 16th of the month but then only having an elevation of ~3 degrees so a very low horizon will be needed and binoculars may well be required to cut through the Sun's glare - but please do not use them until after the Sun has set. It will then have a magnitude of -0.73 and an angular diameter of 5.4 arc seconds.
Mars
Mars. Coming towards the very end of its apparition, Mars can be seen low in the west as darkness falls at the start of the month looking towards the northwest. It then has a magnitude of 1.72 and an angular size of 4.23 arc seconds. As the month progresses, it falls closer to the horizon whilst its magnitude falls to 1.77. With a reduced angular size of 4 arc seconds its elevation will be just 3 degrees after sunset making it hard to spot.
Venus
Venus. As darkness falls at the beginning of the month, Venus will be seen to the north of west shining at magnitude -4.67 at an elevation of ~9 degrees which, of course, varies from south to north across the UK - a variation of 7 degrees in latitude. Its angular size will be 35 arc seconds - a thin crescent. At month's end, whilst it magnitude drops slightly to -4.34, its angular size increases to 53.44 arc seconds - a very thin crescent! It sets at 21:00 BST but may well be lost in the Sun's glare before it becomes visible. Binoculars will probably be needed to spot it, but please do not use them until after the Sun has set.
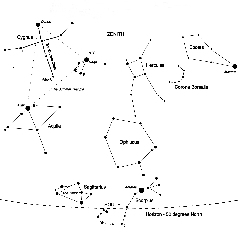
The late evening July Sky
This map shows the constellations seen towards the south at about 10pm BST in mid July. The most prominent star, just a little west of South, is Arcturus in Bootes. It is the second (after Sirius) brightest star in the northern sky. High overhead towards the north (not shown on the chart) and up to the right of Arcturus lies Ursa Major with its prominent grouping of the Plough. As one moves southwards to the left of Bootes one first crosses the constellation Hercules with its magnificent globular cluster, M13, and then across the large but not prominent constellation Ophiucus until, low above the southern horizon lie Sagittarius and Scorpius. Those in the south of the UK - and even better in Southern Europe - will spot the bright red star Antares. Rising in the east is the beautiful region of the Milky Way containing both Cygnus and Lyra. Below is Aquilla. The three bright stars Deneb (in Cygnus), Vega (in Lyra) and Altair (in Aquila) make up the "Summer Triangle".
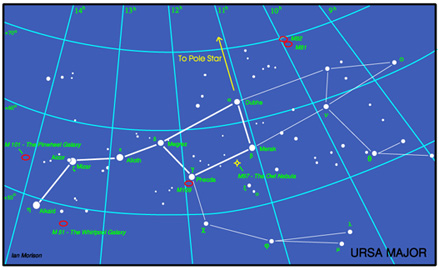
The constellation Ursa Major
The stars of the Plough, shown linked by the thicker lines in the chart above, form one of the most recognised star patterns in the sky. Also called the Big Dipper, after the soup ladles used by farmer's wives in America to serve soup to the farm workers at lunchtime, it forms part of the Great Bear constellation - not quite so easy to make out! The stars Merak and Dubhe form the pointers which will lead you to the Pole Star, and hence find North. The stars Alcor and Mizar form a naked eye double which repays observation in a small telescope as Mizar is then shown to be an easily resolved double star. A fainter reddish star forms a triangle with Alcor and Mizar.
Ursa Major contains many interesting "deep sky" objects. The brightest, listed in Messier's Catalogue, are shown on the chart, but there are many fainter galaxies in the region too. In the upper right of the constellation are a pair of interacting galaxies M81 and M82 shown in the image below. M82 is undergoing a major burst of star formation and hence called a "starburst galaxy". They can be seen together using a low power eyepiece on a small telescope.
Another, and very beautiful, galaxy is M101 which looks rather like a pinwheel firework, hence its other name the Pinwheel Galaxy. It was discovered in1781 and was a late entry to Messier's calalogue of nebulous objects. It is a type Sc spiral galaxy seen face on which is at a distance of about 24 million light years. Type Sc galaxies have a relativly small nucleus and open spiral arms. With an overall diameter of 170,000 light it is one of the largest spirals known (the Milky Way has a diameter of ~ 130,000 light years).
Though just outside the constellation boundary, M51 lies close to Alkaid, the leftmost star of the Plough. Also called the Whirlpool Galaxy it is being deformed by the passage of the smaller galaxy on the left. This is now gravitationally captured by M51 and the two will eventually merge. M51 lies at a distance of about 37 million light years and was the first galaxy in which spiral arms were seen. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1773 and the spiral structure was observed by Lord Rosse in 1845 using the 72" reflector at Birr Castle in Ireland - for many years the largest telescope in the world.
Lying close to Merak is the planetary nebula M97 which is usually called the Owl Nebula due to its resemblance to an owl's face with two large eyes. It was first called this by Lord Rosse who drew it in 1848 - as shown in the image below right. Planetary nebulae ar the remnants of stars similar in size to our Sun. When all possible nuclear fusion processes are complete, the central core collpses down into a "white dwarf" star and the the outer parts of the star are blown off to form the surrounding nebula.
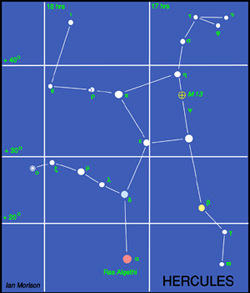
The constellation Hercules
Between the constellation Bootes and the bright star Vega in Lyra lies the constellation Hercules.The Red Giant star Alpha Herculis or Ras Algethi, its arabic name, is one of the largest stars known, with a diameter of around 500 times that of our Sun. In common with most giant stars it varies its size, changing in brightness as it does so from 3rd to 4th magnitude. Lying along one side of the "keystone" lies one of the wonders of the skies, the great globular cluster, M13. Just visible to the unaided eye on a dark clear night, it is easily seen through binoculars as a small ball of cotten wool about 1/3 the diameter of the full Moon. The brightness increases towards the centre where the concentration of stars is greatest. It is a most beautiful sight in a small telescope. It contains around 300,000 stars in a region of space 100 light years across, and is the brightest globular cluster that can be seen in the northern hemisphere.
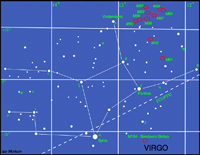
The constellation Virgo
Virgo, in the south-east after sunset this month, is not one of the most prominent constellations, containing only one bright star, Spica, but is one of the largest and is very rewarding for those with "rich field" telescopes capable of seeing the many galaxies that lie within its boundaries. Spica is, in fact, an exceedingly close double star with the two B type stars orbiting each other every 4 days. Their total luminosity is 2000 times that of our Sun. In the upper right hand quadrant of Virgo lies the centre of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. There are 13 galaxies in the Messier catalogue in this region, all of which can be seen with a small telescope. The brightest is the giant elliptical galaxy, M87, with a jet extending from its centre where there is almost certainly a massive black hole into which dust and gas are falling. This releases great amounts of energy which powers particles to reach speeds close to the speed of light forming the jet we see. M87 is also called VIRGO A as it is a very strong radio source.
Below Porrima and to the right of Spica lies M104, an 8th magnitude spiral galaxy about 30 million light years away from us. Its spiral arms are edge on to us so in a small telescope it appears as an elliptical galaxy. It is also known as the Sombrero Galaxy as it looks like a wide brimmed hat in long exposure photographs.
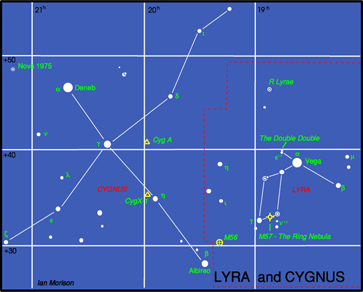
The constellations Lyra and Cygnus
This month the constellations Lyra and Cygnus are rising in the East as darkness falls with their bright stars Vega, in Lyra, and Deneb, in Cygnus, making up the "summer triangle" of bright stars with Altair in the constellation Aquila below. (see sky chart above)
Lyra
Lyra is dominated by its brightest star Vega, the fifth brightest star in the sky. It is a blue-white star having a magnitude of 0.03, and lies 26 light years away. It weighs three times more than the Sun and is about 50 times brighter. It is thus burning up its nuclear fuel at a greater rate than the Sun and so will shine for a correspondingly shorter time. Vega is much younger than the Sun, perhaps only a few hundred million years old, and is surrounded by a cold,dark disc of dust in which an embryonic solar system is being formed!
There is a lovely double star called Epsilon Lyrae up and to the left of Vega. A pair of binoculars will show them up easily - you might even see them both with your unaided eye. In fact a telescope, provided the atmosphere is calm, shows that each of the two stars that you can see is a double star as well so it is called the double double!
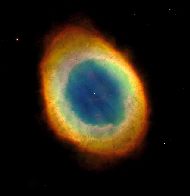
Between Beta and Gamma Lyra lies a beautiful object called the Ring Nebula. It is the 57th object in the Messier Catalogue and so is also called M57. Such objects are called planetary nebulae as in a telescope they show a disc, rather like a planet. But in fact they are the remnants of stars, similar to our Sun, that have come to the end of their life and have blown off a shell of dust and gas around them. The Ring Nebula looks like a greenish smoke ring in a small telescope, but is not as impressive as it is shown in photographs in which you can also see the faint central "white dwarf" star which is the core of the original star which has collapsed down to about the size of the Earth. Still very hot this shines with a blue-white colour, but is cooling down and will eventually become dark and invisible - a "black dwarf"! Do click on the image below to see the large version - its wonderful!
M56 is an 8th magnitude Globular Cluster visible in binoculars roughly half way between Alberio (the head of the Swan) and Gamma Lyrae. It is 33,000 light years away and has a diameter of about 60 light years. It was first seen by Charles Messier in 1779 and became the 56th entry into his catalogue.
Cygnus
Cygnus, the Swan, is sometimes called the "Northern Cross" as it has a distinctive cross shape, but we normally think of it as a flying Swan. Deneb,the arabic word for "tail", is a 1.3 magnitude star which marks the tail of the swan. It is nearly 2000 light years away and appears so bright only because it gives out around 80,000 times as much light as our Sun. In fact if Deneb where as close as the brightest star in the northern sky, Sirius, it would appear as brilliant as the half moon and the sky would never be really dark when it was above the horizon!
The star, Albireo, which marks the head of the Swan is much fainter, but a beautiful sight in a small telescope. This shows that Albireo is made of two stars, amber and blue-green, which provide a wonderful colour contrast. With magnitudes 3.1 and 5.1 they are regarded as the most beautiful double star that can be seen in the sky.
Cygnus lies along the line of the Milky Way, the disk of our own Galaxy, and provides a wealth of stars and clusters to observe. Just to the left of the line joining Deneb and Sadr, the star at the centre of the outstretched wings, you may, under very clear dark skys, see a region which is darker than the surroundings. This is called the Cygnus Rift and is caused by the obscuration of light from distant stars by a lane of dust in our local spiral arm. the dust comes from elements such as carbon which have been built up in stars and ejected into space in explosions that give rise to objects such as the planetary nebula M57 described above.
Deneb,the arabic word for "tail", is a 1.3 magnitude star which marks the tail of the swan. It is nearly 2000 light years away and appears so bright only because it gives out around 80,000 times as much light as our Sun. In fact if Deneb where as close as the brightest star in the northern sky, Sirius, it would appear as brilliant as the half moon and the sky would never be really dark when it was above the horizon!
There is a beautiful region of nebulosity up and to the left of Deneb which is visible with binoculars in a very dark and clear sky. Photographs show an outline that looks like North America - hence its name the North America Nebula. Just to its right is a less bright region that looks like a Pelican, with a long beak and dark eye, so not surprisingly this is called the Pelican Nebula. The photograph below shows them well.
Brocchi's Cluster An easy object to spot with binoculars in Gygnus is "Brocchi's Cluster", often called "The Coathanger",although it appears upside down in the sky! Follow down the neck of the swan to the star Alberio, then sweep down and to its lower left. You should easily spot it against the dark dust lane behind.