The Stars
The Early Evening March Sky
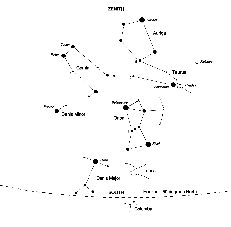
The March Sky in the south - early evening.
This map shows the constellations seen in the south during the early evening. The brilliant constellation of Orion is seen in the south. Moving up and to the right - following the line of the three stars of Orion's belt - brings one to Taurus; the head of the bull being outlined by the V-shaped cluster called the Hyades with its eye delineated by the orange red star Aldebaran. Further up to the right lies the Pleaides Cluster. Towards the zenith from Taurus lies the constellation Auriga, whose brightest star Capella will be nearly overhead. To the upper left of Orion lie the heavenly twins, or Gemini, their heads indicated by the two bright stars Castor and Pollux. Down to the lower left of Orion lies the brightest star in the northern sky, Sirius, in the consteallation Canis Major. Up and to the left of Sirius is Procyon in Canis Minor. Rising in the East is the constellation of Leo, the Lion, with the planet Saturn up and to the right of Regulus its brightest star. Continuing in this direction towards Gemini is the faint constellation of Cancer with its open cluster Praesepe (also called the Beehive Cluster),the 44th object in Messier's catalogue. On a dark night it is a nice object to observe with binoculars. There is also information about the constellation Ursa Major,seen in the north, in the constellation details below.
The Late Evening March Sky
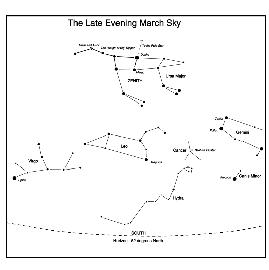
The March Sky in the south - late evening.
This map shows the constellations seen in the south around midnight.
The constellation Gemini is now setting towards the south-west and Leo holds pride (sic) of place in the south with its bright star Regulus. Between Gemini and Leo lies Cancer. It is well worth observing with binoculars to see the Beehive Cluster at its heart. Below Gemini is the tiny constellation Canis Minor whose only bright star is Procyon. Rising in the south-east is the constellation Virgo whose brightest star is Spica. Though Virgo has few bright stars it is in the direction of of a great cluster of galaxies - the Virgo Cluster - which lies at the centre of the supercluster of which our local group of galaxies is an outlying member.
The constellation Gemini
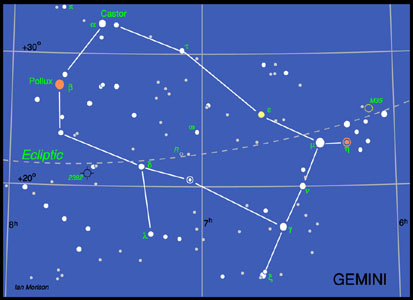 Gemini
Gemini
Gemini - The Twins - lies up and to the left of Orion and is in the south-west during early evenings this month. It contains two bright stars Castor and Pollux of 1.9 and 1.1 magnitudes respectivly. Castor is a close double having a separation of ~ 3.6 arc seconds making it a fine test of the quality of a small telescope - providing the atmospheric seeing is good! In fact the Castor system has 6 stars - each of the two seen in the telescope is a double star, and there is a third, 9th magnitude, companion star 73 arcseconds away which is alos a double star! Pollux is a red giant star of spectral class K0. The planet Pluto was discovered close to delta Geminorum by Clyde Tombaugh in 1930. The variable star shown to the lower right of delta Geminorum is a Cepheid variable, changing its brightness from 3.6 to 4.2 magnitudes with a period of 10.15 days
 M35 and NGC 2158
M35 and NGC 2158
This wonderful image was taken by Fritz Benedict and David Chappell using a 30" telescope at McDonal Observatory. Randy Whited combined the three colour CCD images to make the picture
M35 is an open star cluster comprising several hundred stars around a hundred of which are brighter than magnitude 13 and so will be seen under dark skies with a relativly small telescope. It is easily spotted with binoculars close to the "foot" of the upper right twin. A small telescope at low power using a wide field eyepiece will show it at its best. Those using larger telescopes - say 8 to 10 inches - will spot a smaller compact cluster NGC 2158 close by. NGC 2158 is four times more distant that M35 and ten times older, so the hotter blue stars will have reached the end of their lives leaving only the longer-lived yellow stars like our Sun to dominate its light.
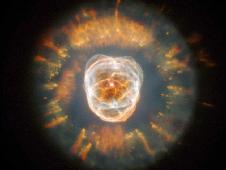 The Eskimo Nebula, NGC2392, Hubble Space Telescope
The Eskimo Nebula, NGC2392, Hubble Space Telescope
To the lower right of the constellation lies the Planetary Nebula NGC2392. As the Hubble Space Telescope image shows, it resembles a head surrounded by the fur collar of a parka hood - hence its other name The Eskimo Nebula. The white dwarf remnant is seen at the centre of the "head". The Nebula was discovered by William Herschel in 1787. It lies about 5000 light years away from us.
The constellation Leo
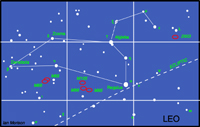 Leo
Leo
The constellation Leo is now in the south-eastern sky in the evening. One of the few constellations that genuinely resembles its name, it looks likes one of the Lions in Trafalger Square, with its main and head forming an arc (called the Sickle) to the upper right, with Regulus in the position of its right knee. Regulus is a blue-white star, five times bigger than the sun at a distance of 90 light years. It shines at magnitude 1.4. Algieba, which forms the base of the neck, is the second brightest star in Leo at magnitude 1.9. With a telescope it resolves into one of the most magnificent double stars in the sky - a pair of golden yellow stars! They orbit their common centre of gravity every 600 years. This lovely pair of orange giants are 170 light years away.
Leo also hosts two pairs of Messier galaxies which lie beneath its belly. The first pair lie about 9 degrees to the west of Regulus and comprise M95 (to the east) and M96. They are almost exactly at the same declination as Regulus so, using an equatorial mount, centre on Regulus, lock the declination axis and sweep towards the west 9 degrees. They are both close to 9th magnitude and may bee seen together with a telescope at low power or individually at higher powers. M65 is a type Sa spiral lying at a distance of 35 millin klight years and M66, considerably bigger than M65, is of type Sb. Type Sa spirals have large nuclei and very tightly wound spiral arms whilst as one moves through type Sb to Sc, the nucleus becomes smaller and the arms more open.
 The galaxies M65 and M66
The galaxies M65 and M66

 M65 - Type Sa spiral, 9.3 magnitude M66 - Type Sb spiral, 8.9 magnitude
M65 - Type Sa spiral, 9.3 magnitude M66 - Type Sb spiral, 8.9 magnitude
The second pair of galaxies, M95 and M96, lie a further 7 degrees to the west between the stars Upsilon and Iota Leonis. M95 is a barred spiral of type SBb. It lies at a distance of 38 million light years and is magnitude 9.7. M96, a type Sa galaxy, is slightly further away at 41 million light years, but a little brighter with a magnitude of 9.2. Both are members of the Leo I group of galaxies and are visible together with a telescope at low power.
 The galaxies M95 and M96
The galaxies M95 and M96

 M95 - Type SBb spiral, 9.7 magnitude M96 - Type Sa spiral, 9.2 magnitude
M95 - Type SBb spiral, 9.7 magnitude M96 - Type Sa spiral, 9.2 magnitude
There is a further ~9th magnitude galaxy in Leo which, surprisingly, is in neither the Messier or Caldwell catalogues. It lies a little below lambda Leonis and was discovered by William Herschel. No 2903 in the New General Catalogue, it is a beautiful type Sb galaxy which is seen at somewhat of an oblique angle. It lies at a distance of 20.5 million light years.
 The 8.9th magnitude, type Sb, Galaxy NGC2903
The 8.9th magnitude, type Sb, Galaxy NGC2903
The constellation Virgo
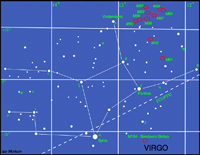 Virgo
Virgo
Virgo, rising in the east in late evening this month, is not one of the most prominent constellations, containing only one bright star, Spica, but is one of the largest and is very rewarding for those with "rich field" telescopes capable of seeing the many galaxies that lie within its boundaries. Spica is, in fact, an exceedingly close double star with the two B type stars orbiting each other every 4 days. Their total luminosity is 2000 times that of our Sun. In the upper right hand quadrant of Virgo lies the centre of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. There are 13 galaxies in the Messier catalogue in this region, all of which can be seen with a small telescope. The brightest is the giant elliptical galaxy, M87, with a jet extending from its centre where there is almost certainly a massive black hole into which dust and gas are falling. This releases great amounts of energy which powers particles to reach speeds close to the speed of light forming the jet we see. M87 is also called VIRGO A as it is a very strong radio source.

 The Giant Elliptical Galaxy M87 HST image showing the jet
The Giant Elliptical Galaxy M87 HST image showing the jet
Below Porrima and to the right of Spica lies M104, an 8th magnitude spiral galaxy about 30 million light years away from us. Its spiral arms are edge on to us so in a small telescope it appears as an elliptical galaxy. It is also known as the Sombrero Galaxy as it looks like a wide brimmed hat in long exposure photographs.
 M104 - The Sombrero Galaxy
M104 - The Sombrero Galaxy
The constellation Ursa Major
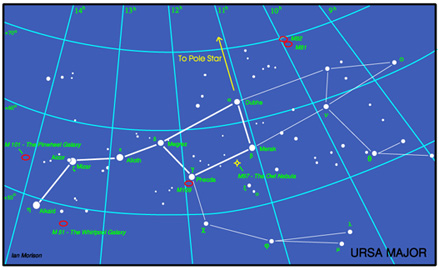 Ursa Major
Ursa Major
The stars of the Plough, shown linked by the thicker lines in the chart above, form one of the most recognised star patterns in the sky. Also called the Big Dipper, after the soup ladles used by farmer's wives in America to serve soup to the farm workers at lunchtime, it forms part of the Great Bear constellation - not quite so easy to make out! The stars Merak and Dubhe form the pointers which will lead you to the Pole Star, and hence find North. The stars Alcor and Mizar form a naked eye double which repays observation in a small telescope as Mizar is then shown to be an easily resolved double star. A fainter reddish star forms a triangle with Alcor and Mizar.
Ursa Major contains many interesting "deep sky" objects. The brightest, listed in Messier's Catalogue, are shown on the chart, but there are many fainter galaxies in the region too. In the upper right of the constellation are a pair of interacting galaxies M81 and M82 shown in the image below. M82 is undergoing a major burst of star formation and hence called a "starburst galaxy". They can be seen together using a low power eyepiece on a small telescope.
 M81 and M82
M81 and M82
Another, and very beautiful, galaxy is M101 which looks rather like a pinwheel firework, hence its other name the Pinwheel Galaxy. It was discovered in1781 and was a late entry to Messier's calalogue of nebulous objects. It is a type Sc spiral galaxy seen face on which is at a distance of about 24 million light years. Type Sc galaxies have a relativly small nucleus and open spiral arms. With an overall diameter of 170,000 light it is one of the largest spirals known (the Milky Way has a diameter of ~ 130,000 light years).
 M101 - The Ursa Major Pinwheel Galaxy
M101 - The Ursa Major Pinwheel Galaxy
Though just outside the constellation boundary, M51 lies close to Alkaid, the leftmost star of the Plough. Also called the Whirlpool Galaxy it is being deformed by the passage of the smaller galaxy on the left. This is now gravitationally captured by M51 and the two will eventually merge. M51 lies at a distance of about 37 million light years and was the first galaxy in which spiral arms were seen. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1773 and the spiral structure was observed by Lord Rosse in 1845 using the 72" reflector at Birr Castle in Ireland - for many years the largest telescope in the world.
 M51 - The Whirlpool Galaxy
M51 - The Whirlpool Galaxy
Lying close to Merak is the planetary nebula M97 which is usually called the Owl Nebula due to its resemblance to an owl's face with two large eyes. It was first called this by Lord Rosse who drew it in 1848 - as shown in the image below right. Planetary nebulae ar the remnants of stars similar in size to our Sun. When all possible nuclear fusion processes are complete, the central core collpses down into a "white dwarf" star and the the outer parts of the star are blown off to form the surrounding nebula.
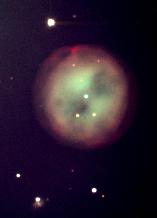
 M97 - The Owl Planetary Nebula Lord Rosse's 1848 drawing of the Owl Nebula
M97 - The Owl Planetary Nebula Lord Rosse's 1848 drawing of the Owl Nebula