The Night Sky February 2011
Compiled by Ian Morison
This page, updated monthly, will let you know some of the things that you can look out for in the night sky. It lists the phases of the Moon, where you will see the naked-eye planets and describes some of the prominent constellations in the night sky during the month.
Image of the Month
Hubble Image of SNR 0509
NASA, ESA, Hubble Heritage Team - J.Hughes (Rutgers University)
This is an image of a supernova remnant in the Large Magellanic Cloud in the southern hemisphere constellation Doradus. It is ~23 light years across and lies at a distance of 160,000 light years. Its progenitor star is thought to have exploded in a type 1a supernovae explosion about 400 years ago - but there are no reports of it having been seen at the time!
Highlights of the Month
Morning February 28th: Venus and a waning crescent Moon
Venus and a thin waning crescent Moon may be seen together in the pre-dawn sky on February 28th.
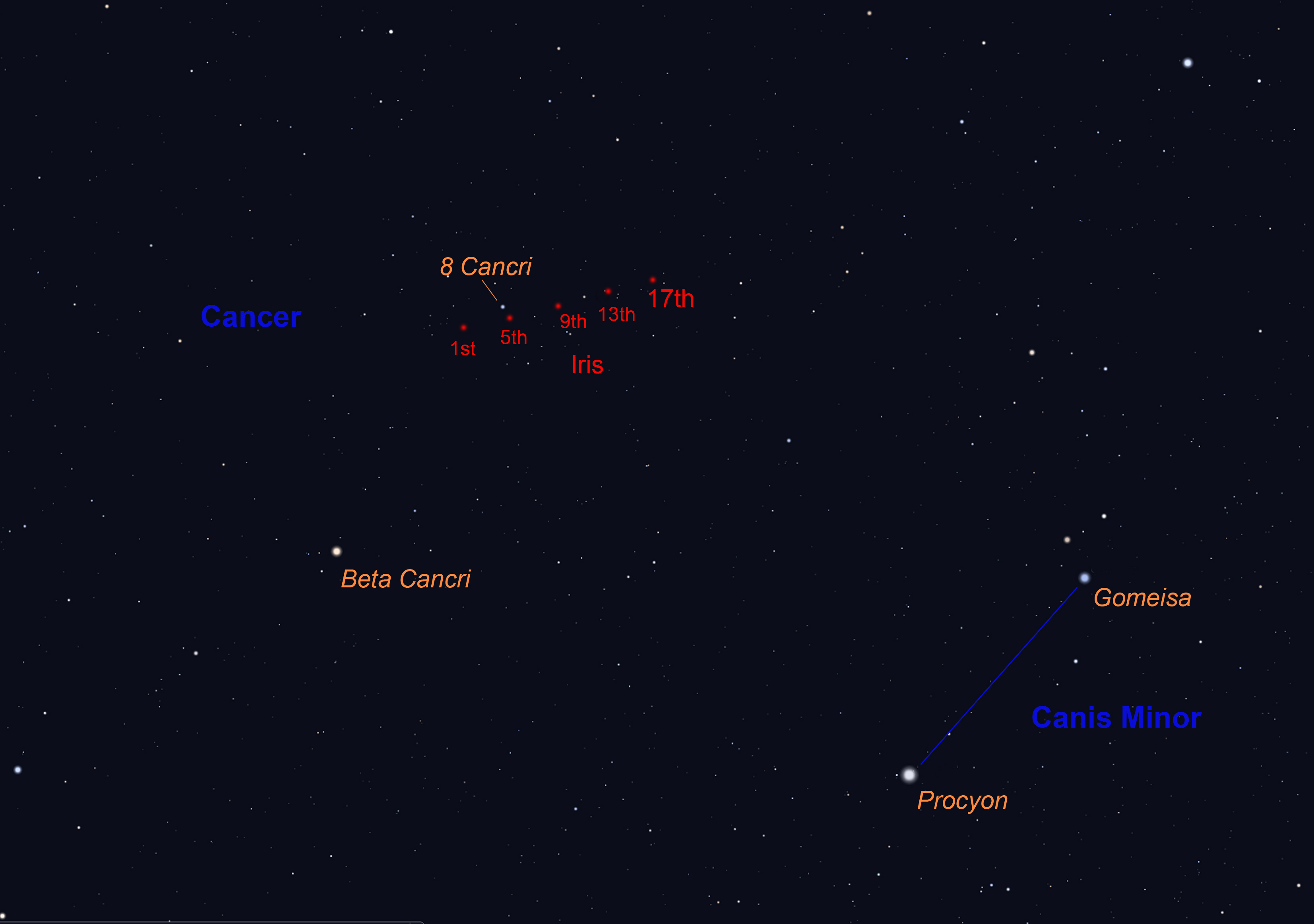
Feb 5th to 12th: Spot an asteroid - No 7, Iris
Asteroid IrisFebruary gives you a chance of spotting the Main Belt Asteroid or Minor Planet Iris, the 7th to have been discovered. Perhaps the best night is on the 5th February when it passes close by the 5th magnitude star 8 Cancri in the constellation Cancer, the Crab. Given a dark transparent night it should be able to spot with binoculars and observations a few hours apart will show that it is moving across to the right against the backdrop of similar brightness stars. The days around Full Moon on the 18th would not be good!
Early Morning 16th February: See the moon occult a star.
Lunar OccultationAt 01:30 on the morning of Feb 16th, the ~5th magnitude star 81 Geminorum will be occultated by the leading (and dark) limb of the Moon. Binoculars would be fine to see the star apparently dissapear.
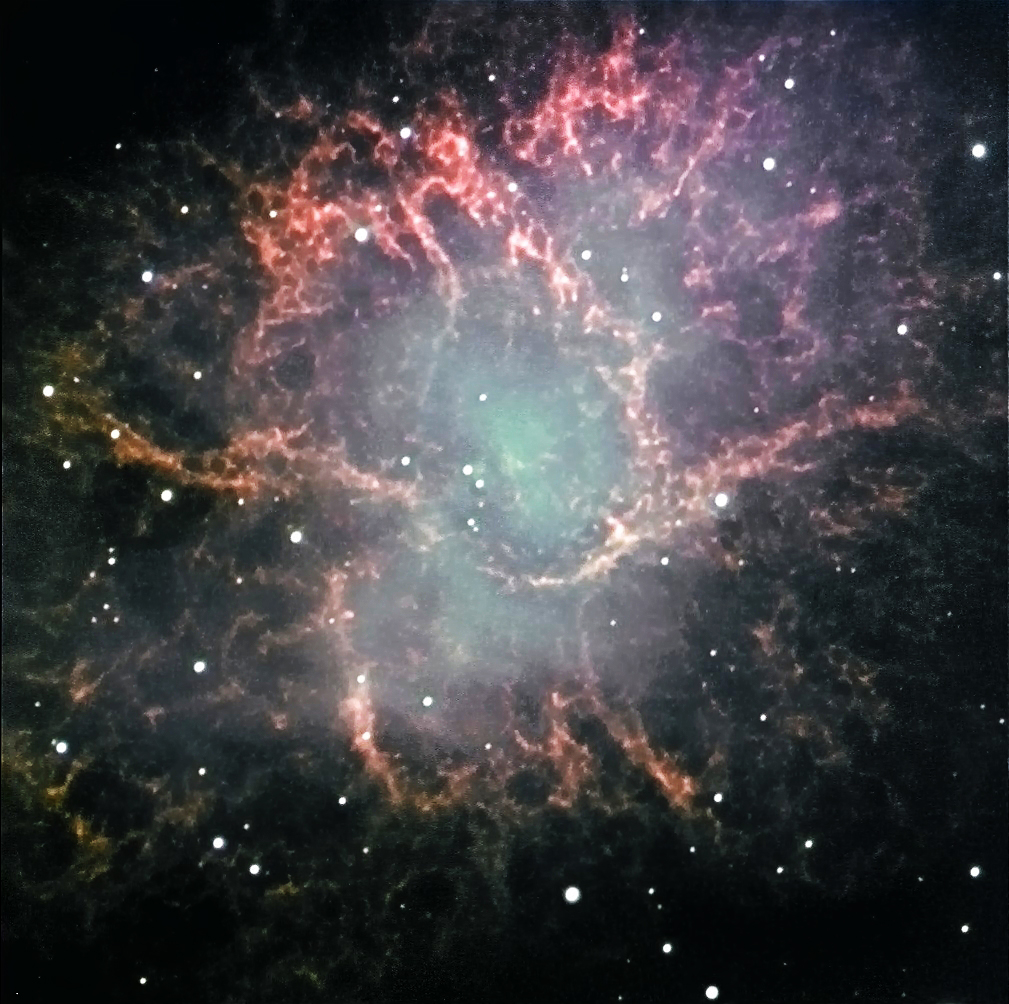
A Messier Object imaged with the Faulkes Telescope: Messier 1 - The Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula, M16, imaged by Nik Szymanek.
This image was taken using the Faulkes Telescope North by Nik Szymanek - one of the UK's leading astro-photograpers. The Crab nebula - the first entry in Charles Messier's catalogue - is the remnant of a supernovae that was seen to explode in the year 1054. It is visible as the lower right of the pair of stars at the centre of the nebula and is a "neutron star" just 30km across but weighing more than our Sun! Under the intense pressure of gravity, the protons and electrons fused to form neutrons and the compact object became stable as gravity was opposed by "neutron degeneracy pressure" - a quantum mechanical force. It is now spinning just under 30 times a second and emitting two opposed beams of light and radio waves which pass across our location in space. We thus detect very regular pulses and so objects like this are called pulsars. At 8.4 magnitudes it is easily seen in a small telescopes under dark transparent skies appearing as a smudge of light which is a little underwhelming to see!
Learn more about the Faulkes Telescopes and how schools can use them: Faulkes Telescope"
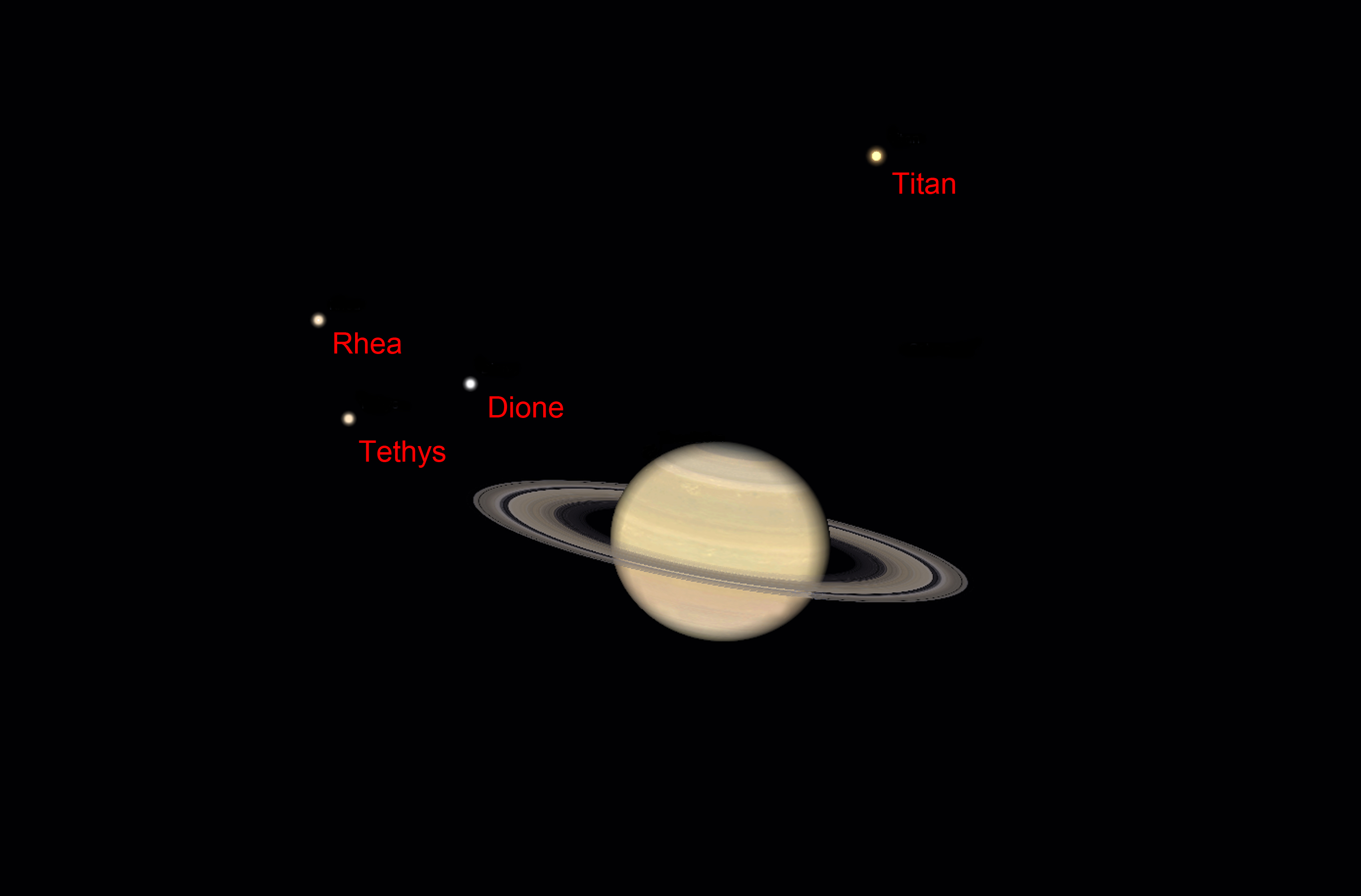
February 5th: 4:30 am: Observe Saturn's Moons
Its easy to spot Titan, Saturn's brightest moon at 8th magnitude - you should be able to do this with binoculars on a dark transparent night away from Full Moon. But given a 6 inch or greater aperture telescope its worth looking for three further satellites: Dione, Rhea and Tethys. The morning of the 5th of February is ideal as there is no Moon and the three 10th magnitude moons make a nice triangle to the east of Saturn with Titan above. Well worth a look if you have a suitable telescope. You can obviously look for them at any other time when the Moon does not intrude. The free software program "Stellarium" (just put into Google) will show you where they will be seen.
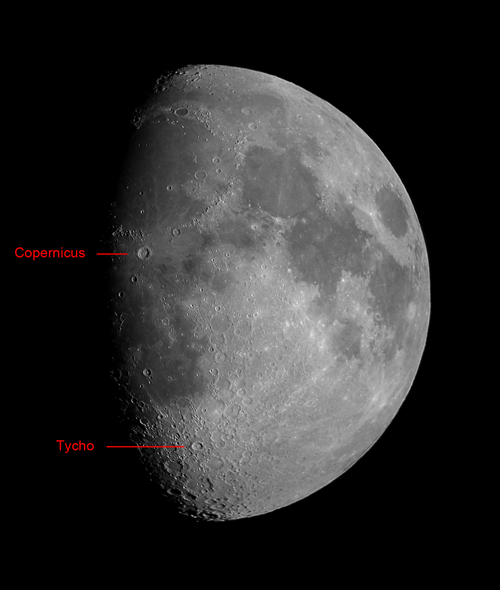
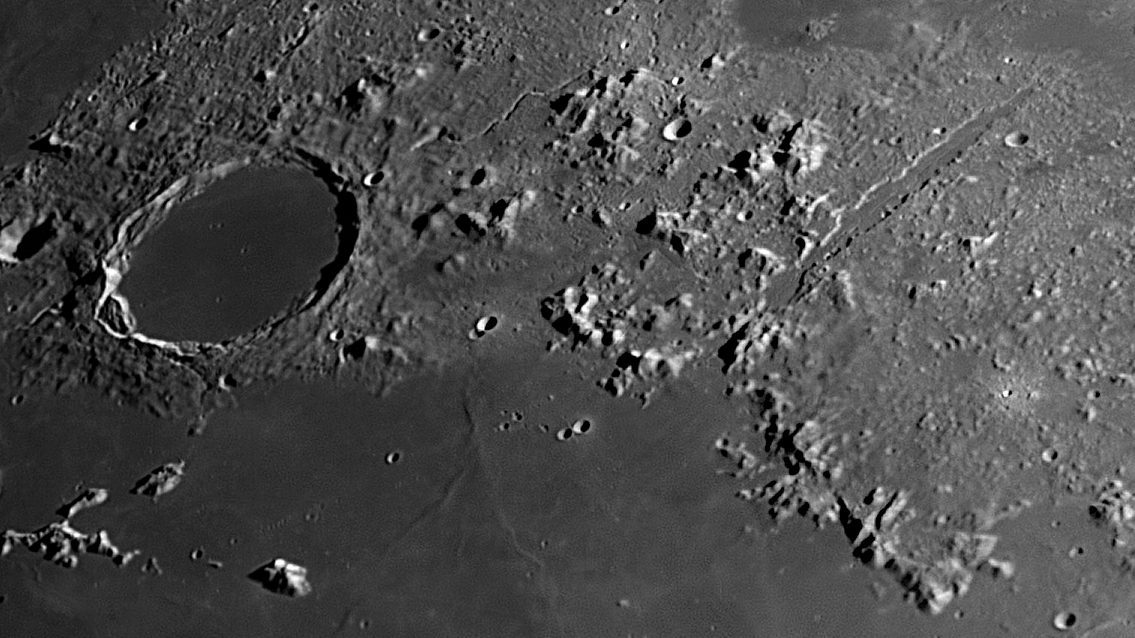
February 14th: Two Great Lunar Craters
Two great Lunar Craters: Tycho and Copernicus
This is a great night to observe two of the greatest craters on the Moon, Tycho and Copernicus, as the terminator is nearby. Tycho is towards the bottom of Moon in a densely cratered area called the Southern Lunar Highlands. It is a relatively young crater which is about 108 million years old. It is interesting in that it is thought to have been formed by the impact of one of the remnents of an asteroid that gave rise to the asteroid Baptistina. Another asteroid originating from the same breakup may well have caused the Chicxulub crater 65 million years ago. It has a diameter of 85 km and is nearly 5 km deep. At full Moon - seen in the image below - the rays of material that were ejected when it was formed can be see arcing across the surface. Copernicus is about 800 million years old and lies in the eastern Oceanus Procellarum beyond the end of the Apennine Mountains. It is 93 km wide and nearly 4 km deep and is a clasic "terraced" crater. Both can be seen with binoculars.
Observe the International Space Station

The International Space Station and Jules Verne passing behind the Lovell Telescope on April 1st 2008.
Image by Andrew Greenwood
Use the link below to find when the space station will be visible in the next few days. In general, the space station can be seen either in the hour or so before dawn or the hour or so after sunset - this is because it is dark and yet the Sun is not too far below the horizon so that it can light up the space station. As the orbit only just gets up the the latitude of the UK it will usually be seen to the south, and is only visible for a minute or so at each sighting. Note that as it is in low-earth orbit the sighting details vary quite considerably across the UK. The NASA website linked to below gives details for several cities in the UK. (Across the world too for foreign visitors to this web page.)
Note: I observed the ISS three times recently and was amazed as to how bright it has become.
Find details of sighting possibilities from your location from: Location Index
See where the space station is now: Current Position
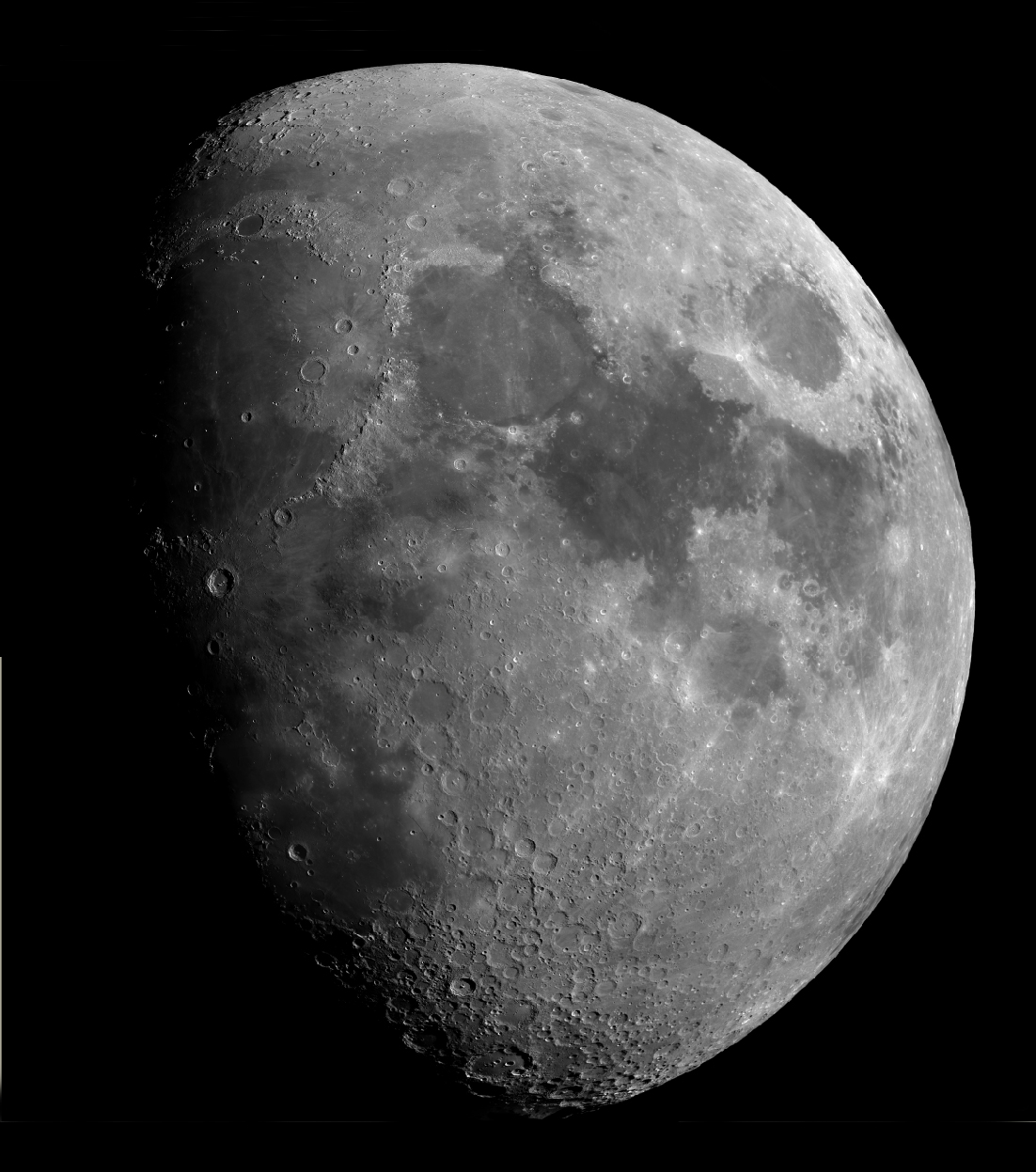
The Moon

The Moon at 3rd Quarter. Image, by Ian Morison, taken with a 150mm Maksutov-Newtonian and Canon G7.
Just below the crator Plato seen near the top of the image is the mountain "Mons Piton". It casts a long shadow across the maria from which one can calculate its height - about 6800ft or 2250m.
| new moon | first quarter | full moon | last quarter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feb 3rd | Feb 11th | Feb 18th | Feb 24th |
Some Lunar Images by Ian Morison, Jodrell Bank Observatory: Lunar Images
A World Record Lunar Image
To mark International Year of Astronomy, a team of british astronomers have made the largest lunar image in history and gained a place in the Guinness Book of Records! The whole image comprises 87.4 megapixels with a Moon diameter of 9550 pixels. This allows details as small as 1km across to be discerned! The superb quality of the image is shown by the detail below of Plato and the Alpine Valley. Craterlets are seen on the floor of Plato and the rille along the centre of the Alpine valley is clearly visible. The image quality is staggering! The team of Damian Peach, Pete lawrence, Dave Tyler, Bruce Kingsley, Nick Smith, Nick Howes, Trevor Little, David Mason, Mark and Lee Irvine with technical support from Ninian Boyle captured the video sequences from which 288 individual mozaic panes were produced. These were then stitched together to form the lunar image.
Please follow the link to the Lunar World Record website and it would be really great if you could donate to Sir Patrick Moore's chosen charity to either download a full resolution image or purchase a print.
The Planets
Jupiter
Jupiter. Jupiter, at magnitude -2.2, can hardly be missed as it dominates the south-western sky after sunset but is now coming towards the end of its current apparition. At the beginning of Febuary it will set at ~21:12 UT but an hour earlier by month's end. You can observe it at an elevation of 30 degrees on the 1st Febuary an hour after sunset, but this will have dropped to 15 degrees by month's end. It becomes a little smaller and a little fainter as the month progresses - down to -2.1 and with an angular size slowly dropping from 35.4 to 34 arc seconds during February. It is still worth observing with a telescope, as Jupiter, having lost its South Equatorial Belt last year is now showing it again though it is still not that prominent. At the same time, the Great Red Spot has intensified its colour so is now standing out very well! A small telescope will easily pick up Jupiter's four Galilean moons as they weave their way around it. The thin waxing crescent Moon passes close to Jupiter on the 6th and 7th of the month.
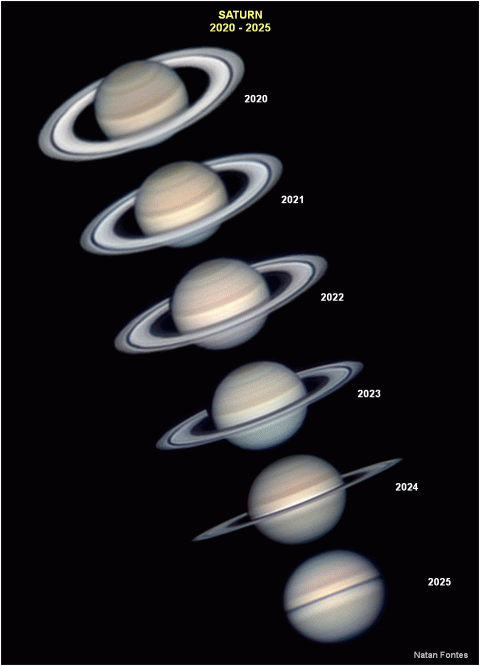
Saturn
Saturn. Saturn is becoming a late evening object rising at ~22:30 at the beginning of the month and 21:00 by Februar's end. It starts February with a magnitude of +0.6. As the month progresses, its brightness increases a touch to +0.5. Compared to last year, its apparent brightness is now increasing as the rings are now opening out again - now tilted more than 10 degrees from edge They span an angular size of 42 arc seconds at mid-month - over double the 19 arc seconds of the planet's disc. Given a small telescope it should now be possible to see Cassini's division - a dark band that separates the A and B rings. It will also show Saturn's brightest moon, Titan, at magnitude +8. It will lie above the planet on the 5th and 21st and below on the 12th and 28th. A 6 inch or more diameter scope will, under dark skies, show three other moons;Tethys, Dione and Rhea. On the night of the 4th/5th they will form a tight triangle to the left of Saturn.
See Highlight above.
Mercury
Mercury passes behind the Sun on February25th, so will not be visible this month
Mars
Mars lies behind the Sun and will be at superior conjunction (directly behind the Sun) on the 4th of February so will not be visible this month.
Venus
Venus is now a pre-dawn object shining at a magnitude of -4.2 at the beginning of the month. It rises a couple of hours before sunrise, and, as the ecliptic at dawn makes a steep angle with the horizon at this time of the year, it is seen high in the sky at dawn. At the beginning of February, its angular size is 19 arc seconds across and 61% illuminated This reduces to 16.3 arc seconds by month's end but, at the same time, its illumination increases to 71% so the magnitude only drops to -4.1. Venus stays at much the same brightness (-4 to -4.5) for much of its apparition as, when it is further from us and so has a smaller angular size, more of its disk is illuminated giving a roughly constant illuminated area.
See Highlight above.
Find more planetary images and details about the Solar System: The Solar System
The Stars
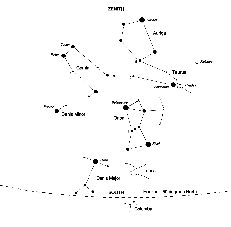
The Mid Evening February Sky
This map shows the constellations seen in the south during the evening. The brilliant constellation of Orion is seen in the south. Moving up and to the right - following the line of the three stars of Orion's belt - brings one to Taurus; the head of the bull being outlined by the V-shaped cluster called the Hyades with its eye delineated by the orange red star Aldebaran. Further up to the right lies the Pleaides Cluster. Towards the zenith from Taurus lies the constellation Auriga, whose brightest star Capella will be nearly overhead. To the upper left of Orion lie the heavenly twins, or Gemini, their heads indicated by the two bright stars Castor and Pollux. Down to the lower left of Orion lies the brightest star in the northern sky, Sirius, in the consteallation Canis Major. Up and to the left of Sirius is Procyon in Canis Minor. Rising in the East is the constellation of Leo, the Lion, with the planet Saturn up and to the right of Regulus its brightest star. Continuing in this direction towards Gemini is the faint constellation of Cancer with its open cluster Praesepe (also called the Beehive Cluster),the 44th object in Messier's catalogue. On a dark night it is a nice object to observe with binoculars. There is also information about the constellation Ursa Major,seen in the north, in the constellation details below.
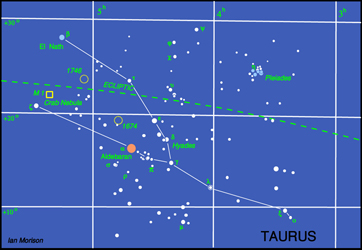
The constellation Taurus
Taurus is one of the most beautiful constellations and you can almost imagine the Bull charging down to the left towards Orion. His face is delineated by the "V" shaped cluster of stars called the Hyades, his eye is the red giant star Aldebaran and the tips of his horns are shown by the stars beta and zeta Tauri. Although alpha Tauri, Aldebaran, appears to lie amongst the stars of the Hyades cluster it is, in fact, less than half their distance lying 68 light years away from us. It is around 40 times the diameter of our Sun and 100 times as bright.
To the upper right of Taurus lies the open cluster, M45, the Pleiades. Often called the Seven Sisters, it is one of the brightest and closest open clusters. The Pleiades cluster lies at a distance of 400 light years and contains over 3000 stars. The cluster, which is about 13 light years across, is moving towards the star Betelgeuse in Orion. Surrounding the brightest stars are seen blue reflection nebulae caused by reflected light from many small carbon grains. These relfection nebulae look blue as the dust grains scatter blue light more efficiently than red. The grains form part of a molecular cloud through which the cluster is currently passing. (Or, to be more precise, did 400 years ago!)
Close to the tip of the left hand horn lies the Crab Nebula, also called M1 as it is the first entry of Charles Messier's catalogue of nebulous objects. Lying 6500 light years from the Sun, it is the remains of a giant star that was seen to explode as a supernova in the year 1056. It may just be glimpsed with binoculars on a very clear dark night and a telescope will show it as a misty blur of light.
Its name "The Crab Nebula" was given to it by the Third Earl of Rosse who observed it with the 72 inch reflector at Birr Castle in County Offaly in central Ireland. As shown in the drawing above, it appeared to him rather lile a spider crab. The 72 inch was the world's largest telelescope for many years. At the heart of the Crab Nebula is a neutron star, the result of the collapse of the original star's core. Although only around 20 km in diameter it weighs more than our Sun and is spinning 30 times a second. Its rotating magnetic field generate beams of light and radio waves which sweep across the sky. As a result, a radio telescope will pick up very regular pulses of radiation and the object is thus also known a Pulsar. Its pulses are monitored each day at Jodrell Bank with a 13m radio telescope.
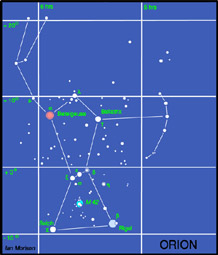
The constellation Orion
Orion, perhaps the most beautiful of constellations, will be seen in the south at around 11 - 12 pm during January. Orion is the hunter holding up a club and shield against the charge of Taurus, the Bull up and to his right. Alpha Orionis, or Betelgeuse, is a read supergiant star varying in size between three and four hundred times that of our Sun. The result is that its brightness varies somewhat. Beta Orionis, or Rigel, is a blue supergiant which, at around 1000 light years distance is about twice as far away as Betelgeuse. It has a 7th magnitude companion. The three stars of Orion's belt lie at a distance of around 1500 light years. Just below the lower left hand star lies a strip of nebulosity against which can be seen a pillar of dust in the shape of the chess-board knight. It is thus called the Horsehead Nebula. It shows up very well photographically but is exceedingly difficult to see visually - even with relativly large telescope.
Beneath the central star of the belt lies Orion's sword containing one of the most beautiful sights in the heavens - The Orion Nebula. It is a region of star formation and the reddish colour seen in photographs comes from Hydrogen excited by ultraviolet emitted from the very hot young stars that make up the Trapesium which is at its heart. The nebula, cradling the trapesium stars, is a beautiful sight in binoculars or, better still, a telescope. To the eye it appears greenish, not red, as the eye is much more sensitive to the green light emitted by ionized oxygen than the reddish glow from the hydrogen atoms.
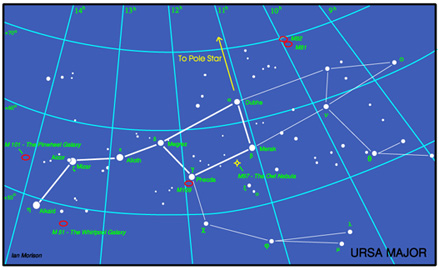
The constellation Ursa Major
The stars of the Plough, shown linked by the thicker lines in the chart above, form one of the most recognised star patterns in the sky. Also called the Big Dipper, after the soup ladles used by farmer's wives in America to serve soup to the farm workers at lunchtime, it forms part of the Great Bear constellation - not quite so easy to make out! The stars Merak and Dubhe form the pointers which will lead you to the Pole Star, and hence find North. The stars Alcor and Mizar form a naked eye double which repays observation in a small telescope as Mizar is then shown to be an easily resolved double star. A fainter reddish star forms a triangle with Alcor and Mizar.
Ursa Major contains many interesting "deep sky" objects. The brightest, listed in Messier's Catalogue, are shown on the chart, but there are many fainter galaxies in the region too. In the upper right of the constellation are a pair of interacting galaxies M81 and M82 shown in the image below. M82 is undergoing a major burst of star formation and hence called a "starburst galaxy". They can be seen together using a low power eyepiece on a small telescope.
Another, and very beautiful, galaxy is M101 which looks rather like a pinwheel firework, hence its other name the Pinwheel Galaxy. It was discovered in1781 and was a late entry to Messier's calalogue of nebulous objects. It is a type Sc spiral galaxy seen face on which is at a distance of about 24 million light years. Type Sc galaxies have a relativly small nucleus and open spiral arms. With an overall diameter of 170,000 light it is one of the largest spirals known (the Milky Way has a diameter of ~ 130,000 light years).
Though just outside the constellation boundary, M51 lies close to Alkaid, the leftmost star of the Plough. Also called the Whirlpool Galaxy it is being deformed by the passage of the smaller galaxy on the left. This is now gravitationally captured by M51 and the two will eventually merge. M51 lies at a distance of about 37 million light years and was the first galaxy in which spiral arms were seen. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1773 and the spiral structure was observed by Lord Rosse in 1845 using the 72" reflector at Birr Castle in Ireland - for many years the largest telescope in the world.
Lying close to Merak is the planetary nebula M97 which is usually called the Owl Nebula due to its resemblance to an owl's face with two large eyes. It was first called this by Lord Rosse who drew it in 1848 - as shown in the image below right. Planetary nebulae ar the remnants of stars similar in size to our Sun. When all possible nuclear fusion processes are complete, the central core collpses down into a "white dwarf" star and the the outer parts of the star are blown off to form the surrounding nebula.